 Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
 Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) is a perennial herbaceous legume that has been cultivated since at least ancient Greek and Roman times. It is one of the world’s most important forage species, due to its high nutritional quality, yields, and adaptability1. As a major forage protein source for livestock, alfalfa is cultivated over 80 countries with coverage exceeding 30 million hectares. It is the third most valuable (7.8–10.8 billion dollars) and the fourth most widely grown (8.7 million hectares) field crop in the USA, after corn, soybean, and wheat. Rapid increases in livestock production have also greatly increased demands for alfalfa forage in developing countries such as China in the last 50 years. In addition to its high value as fodder, alfalfa cultivation is important for improving soil quality in appropriate areas. Therefore, alfalfa has the potential to improve global food security as well as being a commercially valuable crop in its own right.
Recently, an “allele-aware” tetraploid genome assembly has been published (Chen et al. 2020), using PacBio Circular Consensus Sequencing (CCS) technology and Hi-C scaffolding, that was able to assemble all 32 chromosomes representing the four different haplotypes of each of the 8 base chromosomes. The sequenced accession is XinJiangDaYe, a large-leaved alfalfa cultivar from Xinjiang Provence of northwest China that has good regeneration properties
Choromsome number: 8*4=32 (comprising eight homologous groups with four allelic chromosomes in each)
Estimated genome size: 2.738 Gb
Contig N50: 459 kb
Protein-coding genes: 164,632
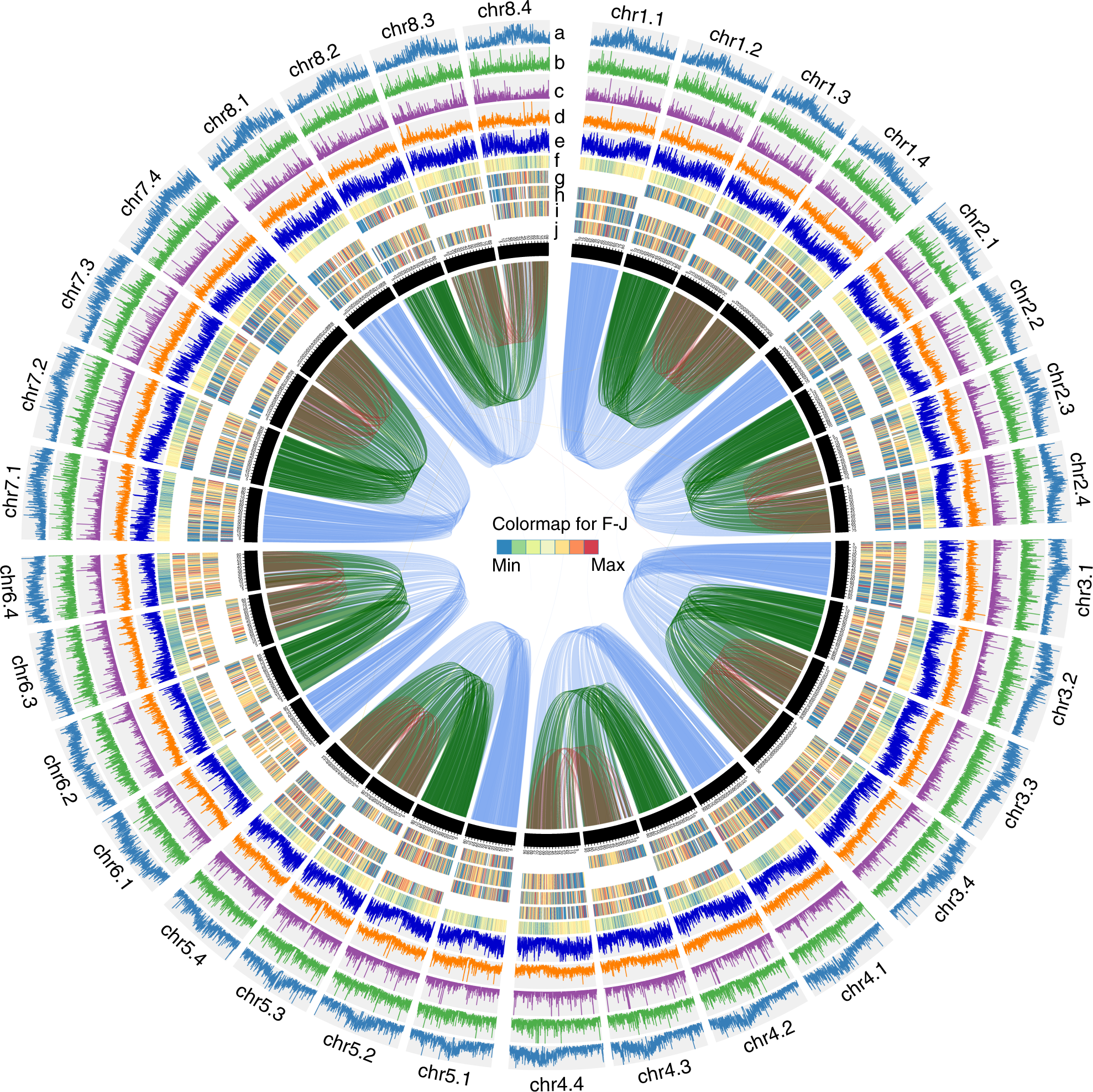
Fig. 1: Overview of the cultivated alfalfa genome.
The tracks indicate (moving inwards): a density of LTR transposons, b density of LINE transposons, c density of SINE transposons, d density of DNA transposons, e gene density, f gene expression levels, g Ka/Ks of syntenic gene pairs identified between chrX.1 and one of chrX.2, chrX.3, chrX.4, h Ka/Ks of syntenic gene pairs identified between chrX.2 and one of chrX.1, chrX.3, chrX.4, i Ka/Ks of syntenic gene pairs identified between chrX.3 and one of chrX.1, chrX.2, chrX.4, and j Ka/Ks of syntenic gene pairs identified between chrX.4 and one of chrX.1, chrX.2, chrX.3. Links in the core connect synteny blocks, blue ribbons indicate synteny blocks between chrX.1 and chrX.2, chrX.3, chrX.4, green ribbons indicate synteny blocks between chrX.2 and chrX.3, chrX.4, red ribbons indicate synteny blocks between chrX.3 and chrX.4. Source data are provided as a Source data file.
Reference:
You can use Gene ID (e.g. MS.gene059669)