 Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
 Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
The M. sativa complex is composed of perennial, outcrossing, morphologically differentiated, but often interfertile taxa. The M. sativa complex includes diploid and autotetraploid subspecies. For instance, M. sativa ssp. caerulea is a diploid subspecies that has been identified as the ancestor of tetraploid cultivated alfalfa. By comparison, cultivated alfalfa (M. sativa ssp. sativa, 2n = 4× = 32) is a true autotetraploid that shows quadrivalents during meiosis and tetrasomic inheritance. These subspecies hybrids display heterosis for many quantitative traits.
Here, researcher present a high-quality, chromosome-level haploid genome assembly for M. sativa ssp. sativa cv. Zhongmu No. 1, a widely grown cultivar in Northern China. This assembly consists of eight pseudo-chromosomes.
Choromsome number: 8
Estimated genome size: 816 Mb
Contig N50: 3.92 Mb
Protein-coding genes: 49,165
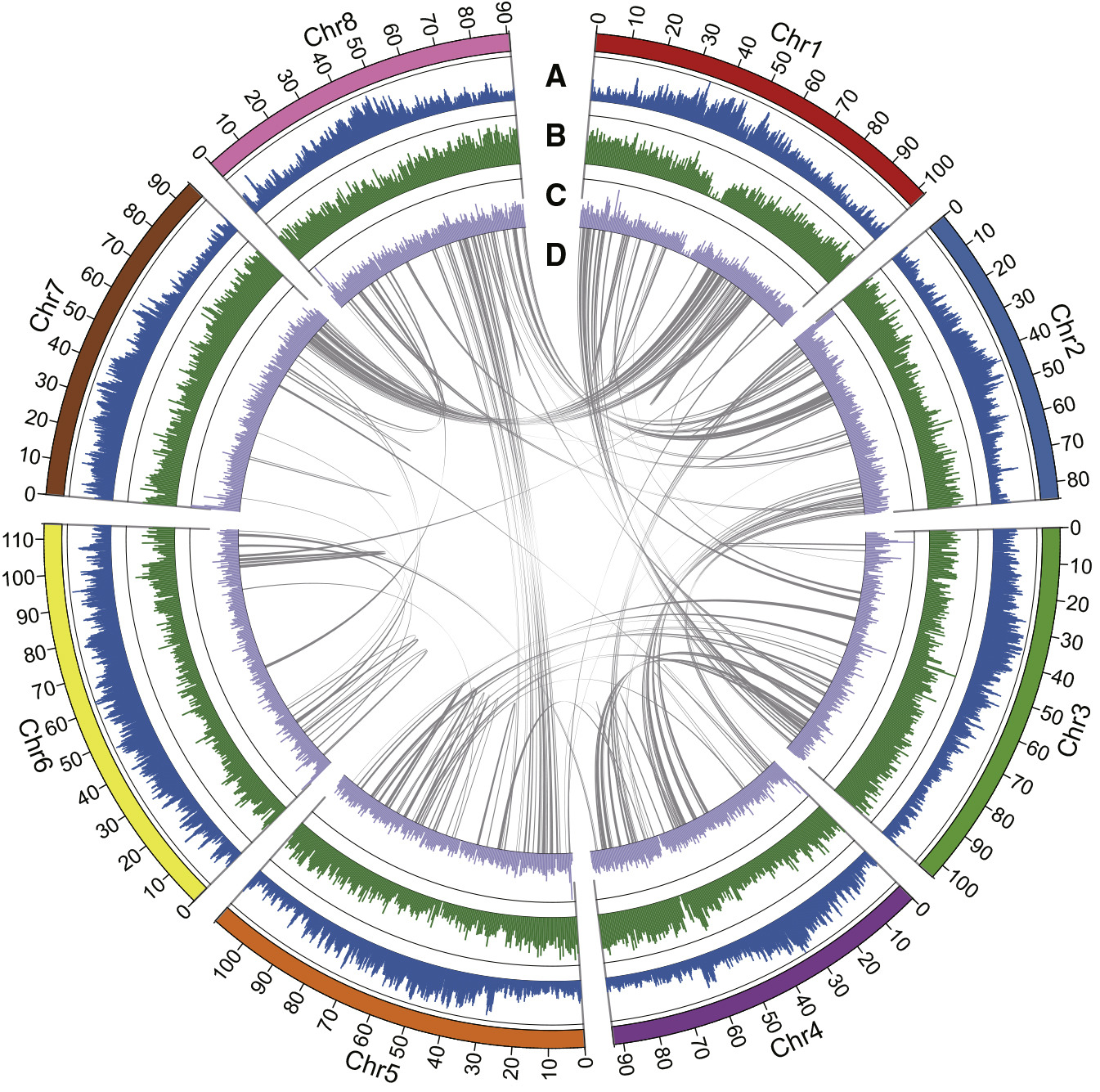
Figure 1 Distribution of Genomic Features within the Alfalfa Zhongmu No. 1 Genome.
(A–C) Circular representation of the GC content (A), gene density (B), and LTR density (C) of genome regions (100 kb for each window). (D) Collinear gene blocks in the Zhongmu No. 1 genome.
Reference:
You can use Gene ID (e.g. MsG0380016624.01)