 Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
 Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Alfalfa Gene Editing Database
Cultivated alfalfa is a cross-pollinated perennial autotetraploid (2n = 4× = 32) species. The complex genetic feature of alfalfa makes it difficult to develop new cultivars using an efficient breeding strategy. Two recently published draft genomes of the autopolyploid alfalfa, Xinjiangdaye and Zhongmu-1, provide valuable information for related studies of alfalfa. The Xinjiangdaye genome was assembled at the allele-aware chromosome level using the ALLHiC algorithm, whereas the Zhongmu-1 genome was merely assembled at the haploid chromosome level. Compared with several other plants such as maize and rice, the genomic information of cultivated alfalfa is still limited. In this study, researcher assembled the allele-aware chromosome-level genome sequence of the Chinese alfalfa cultivar Zhongmu-4, which is one of the most common alfalfa cultivars grown in northern China because of its high yield and salt tolerance.
Advantages of this cultivar include its greater root system, large leaf area, high nutritional value (about 20% crude protein content), fast regeneration, high yield, and salt tolerance. Zhongmu-4 alfalfa is widely cultivated in the Huang-Huai-Hai region of China. The mean annual hay yield can reach 15.0–17.4 t/ha, which is about 10% greater than that of Zhongmu-1. By the end of 2020, the total planting area of Zhongmu-4 has exceeded 200,000 ha.
Choromsome number: 32
Estimated genome size: 2.56Gb
Contig N50: 2.06 Mb
Protein-coding genes: 146,704
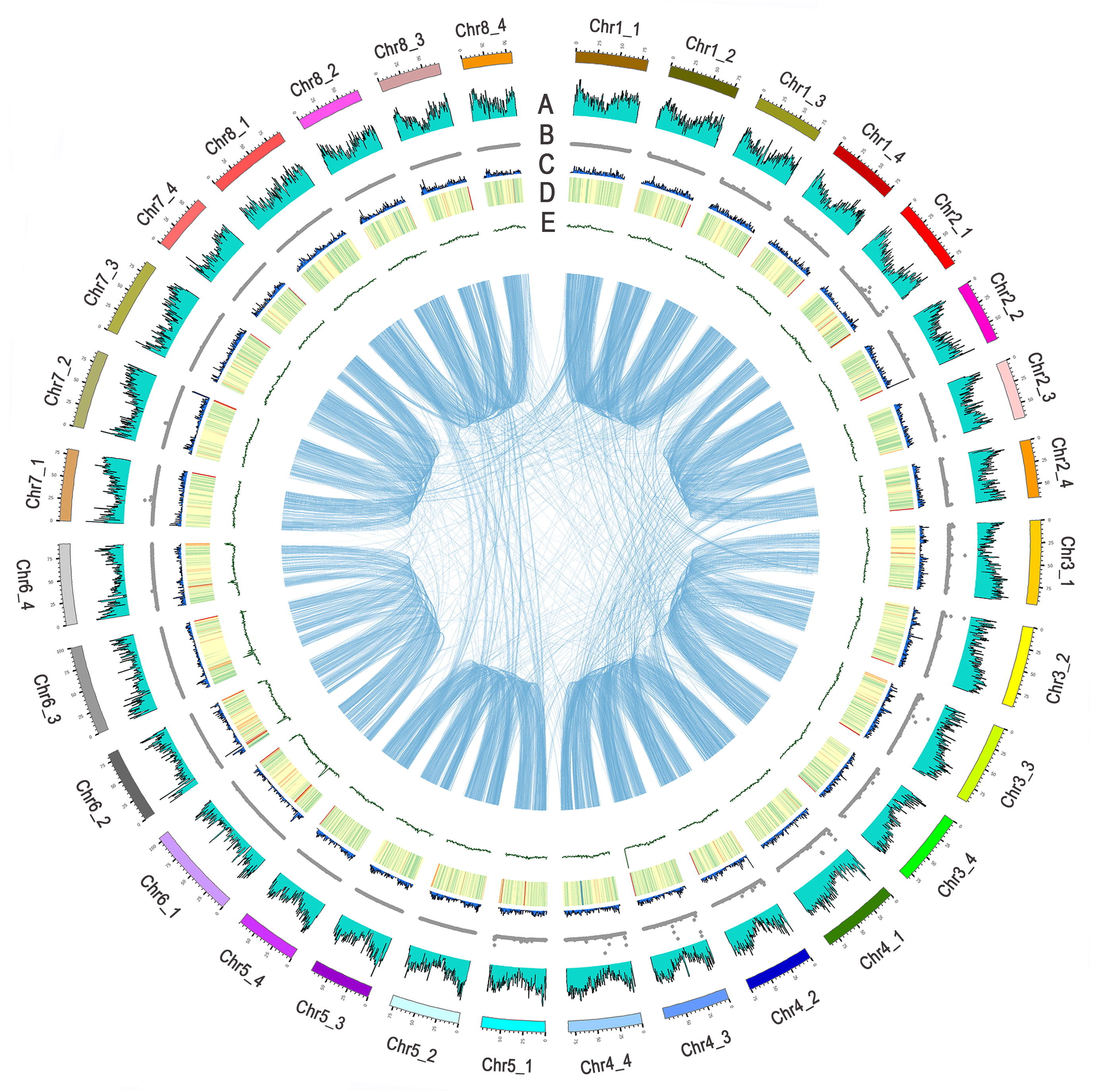
Figure 1. Distribution of Zhongmu-4 genomic features
A. Density of annotated genes. B. Density of filtered SNPs in the GWAS population. C. Density of syntenic paralogous gene pairs with a Ka/Ks ratio > 1. D. Density of repetitive sequences. E. GC content density. Synteny blocks are linked in the center. The outermost bars represent the length (Mb) of chromosomes. SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; GWAS, genome-wide association study; Ka, the number of nonsynonymous substitutions per nonsynonymous site; Ks, the number of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site.
Reference:
You can use Gene ID (e.g. Msa1344880)